When importing goods from China or any other country, understanding how shipping costs are calculated is crucial. Freight carriers use chargeable weight, which can be either the actual weight (gross weight) or the volume weight (dimensional weight), depending on which is higher. Misunderstanding this concept can lead to unexpected shipping costs.
In this guide, we will explain the difference between chargeable weight and volume weight, how they are calculated, and strategies to minimize shipping expenses.
What is Chargeable Weight?

Chargeable weight is the weight used by freight carriers to determine the shipping cost. It is the higher value between:
- Gross weight (Actual weight) – The physical weight of the shipment measured in kilograms (kg) or pounds (lbs).
- Volume weight (Dimensional weight) – A calculated weight based on the cargo’s dimensions.
Why Do Freight Companies Use Chargeable Weight?
- Cargo with a large volume but low actual weight
e.g., pillows or plastic products: takes up significant space in an aircraft or container. Freight carriers use chargeable weight to ensure they are compensated fairly for the space occupied. This prevents shipping companies from losing revenue on lightweight yet bulky items that consume valuable cargo space.
- Conversely, cargo with a high actual weight but small volume
e.g., metal ingots, batteries, or machinery parts also affects freight pricing. Each aircraft and container has strict weight limits. Even if these items do not take up much space, they contribute significantly to the total allowable weight, potentially reducing the total number of shipments that can be loaded.
By using chargeable weight, freight carriers maintain a balance between space usage and weight capacity, ensuring fair pricing and efficient cargo distribution.
How to Calculate Volume Weight?

Volume weight (or dimensional weight) is calculated using different formulas depending on the transportation mode:
Air Freight Chargeable Weight Calculation
For air freight, the volume weight formula is:
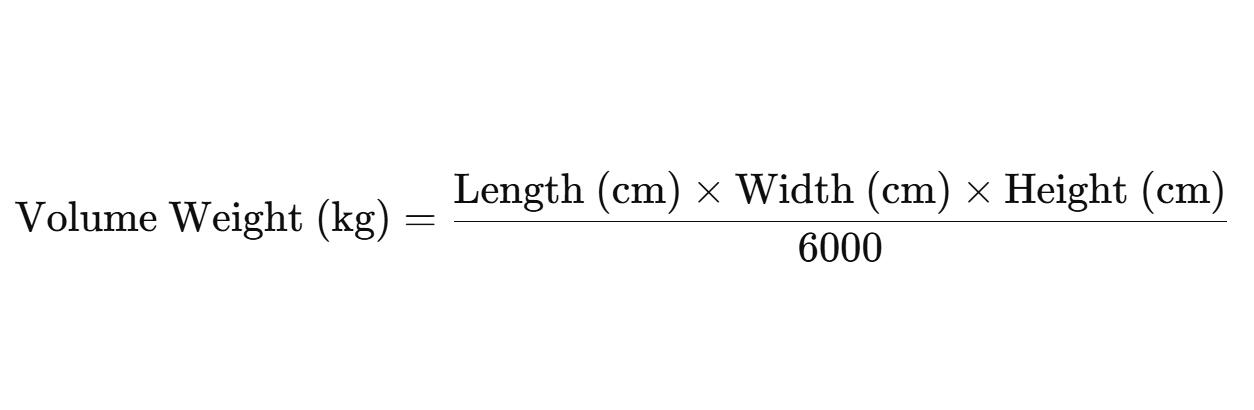
Example 1: Actual Weight is Greater
Shipment Details:
| Number of Cartons | Dimensions (L×W×H) cm | Per Carton Actual Weight (kg) | Total Actual Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 30 × 40 × 50 | 18 | 360 |
Volume Weight Calculation:
The volume weight is calculated using the formula:
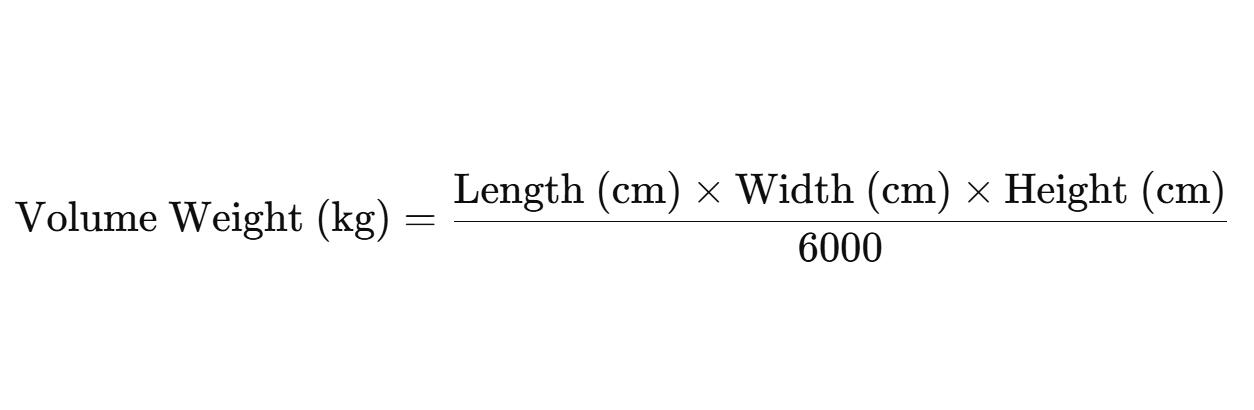
For one carton:
Volume weight = 30 x 40 x 50/6000 = 10kg
For 20 cartons:
Volume weight = 20cartons x 10kg/carton =200kg
Final Chargeable Weight:
| Total Actual Weight (kg) | Total Volume Weight (kg) | Chargeable Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 360 | 200 | 360 (Actual Weight) |
Since the actual weight (360 kg) is greater than the volume weight (200 kg), the chargeable weight is 360 kg.
Example 2: Volume Weight is Greater
Shipment Details:
| Number of Cartons | Dimensions (L×W×H) cm | Per Carton Actual Weight (kg) | Total Actual Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 40 × 50 × 60 | 18 | 360 |
Volume Weight Calculation:
For one carton:
Volume weight = 40 x 50 x 60/6000 = 20kg
For 20 cartons:
Volume weight = 20cartons x 20kg/carton =400kg
Final Chargeable Weight:
| Total Actual Weight (kg) | Total Volume Weight (kg) | Chargeable Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 360 | 400 | 400 (Volume Weight) |
Since the volume weight (400 kg) is greater than the actual weight (360 kg), the chargeable weight is 400 kg.
Sea Freight (to Port) Calculation

For traditional sea freight to port (LCL shipping), the volume weight formula is:
1CBM = 1000kg
If a shipment is 1.5 CBM, its chargeable weight would be:
*1.5 1000 = 1500 kg**
For FCL (Full Container Load), chargeable weight is typically based on actual weight.
Sea Freight DDP Chargeable Weight Calculation

For DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) sea freight, the chargeable weight is determined by comparing actual weight and volume weight. Below are two examples demonstrating how to calculate the chargeable weight.
Example 1: Actual Weight is Greater
Shipment Details:
| Number of Cartons | Dimensions (L×W×H) cm | Per Carton Actual Weight (kg) | Total Actual Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 40 × 40 × 50 | 26 | 780 |
Volume Weight Calculation:
The volume weight is calculated using the formula:
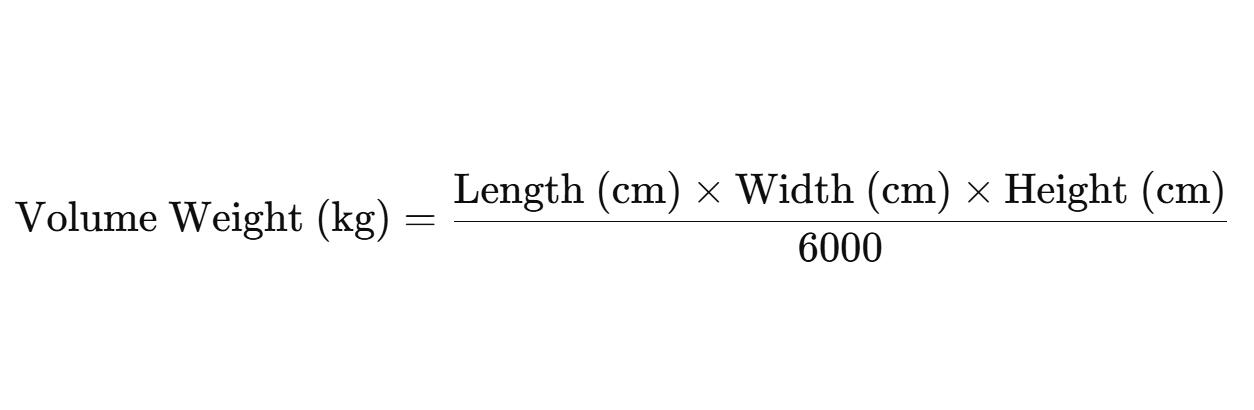
For one carton:
Volume weight = 40 x 40 x 50/6000 = 13.5kg
For 30 cartons:
Volume weight = 30cartons x 13.5kg/carton =405kg
Final Chargeable Weight:
| Total Actual Weight (kg) | Total Volume Weight (kg) | Chargeable Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 780 | 405 | 780 (Actual Weight) |
Since the actual weight (780 kg) is greater than the volume weight (405 kg), the chargeable weight is 780 kg.
Example 2: Volume Weight is Greater
Shipment Details:
| Number of Cartons | Dimensions (L×W×H) cm | Per Carton Actual Weight (kg) | Total Actual Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 80 × 60 × 60 | 20 | 600 |
Volume Weight Calculation:
For one carton:
Volume weight = 80 x 60 x 60/6000 = 48kg
For 30 cartons:
Volume weight = 30cartons x 48kg/carton =1440kg
Final Chargeable Weight:
| Total Actual Weight (kg) | Total Volume Weight (kg) | Chargeable Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 600 | 1440 | 1440 (Volume Weight) |
Since the volume weight (1440 kg) is greater than the actual weight (600 kg), the chargeable weight is 1440 kg.
So if you still don’t understand, check this below:
- If actual weight > volume weight, chargeable weight = actual weight.
- If volume weight > actual weight, chargeable weight = volume weight.
This method ensures that bulky but lightweight shipments are charged based on their space utilization, while dense shipments are charged by their actual mass.
Express Courier (DHL, FedEx, UPS) Chargeable weight

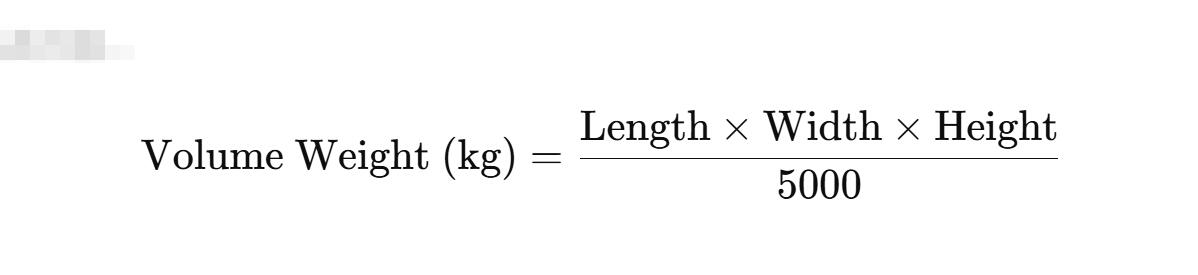
Express couriers use a divisor of 5000 instead of 6000:
Example 1: Actual Weight is Greater
Shipment Details:
| Number of Cartons | Dimensions (L×W×H) cm | Per Carton Actual Weight (kg) | Total Actual Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 30 × 40 × 50 | 15 | 120 |
Volume Weight Calculation:
The volume weight is calculated using the formula:
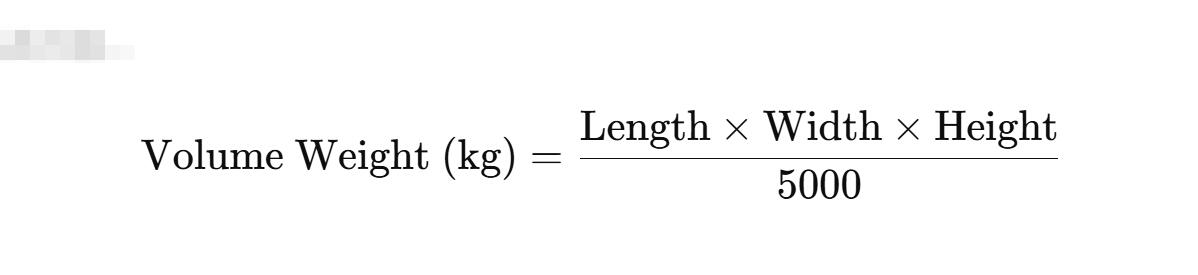
For one carton:
Volume weight = 30 x 40 x 50/5000 = 12kg
For 8 cartons:
Volume weight = 8cartons x 12kg/carton =96kg
Final Chargeable Weight:
| Total Actual Weight (kg) | Total Volume Weight (kg) | Chargeable Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 120 | 96 | 120 (Actual Weight) |
Since the actual weight (120 kg) is greater than the volume weight (96 kg), the chargeable weight is 120 kg.
Example 2: Volume Weight is Greater
Shipment Details:
| Number of Cartons | Dimensions (L×W×H) cm | Per Carton Actual Weight (kg) | Total Actual Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 40 × 50 × 50 | 15 | 120 |
Volume Weight Calculation:
For one carton:
Volume weight = 40 x 50 x 50/5000 = 20kg
For 8 cartons:
Volume weight = 8cartons x 20kg/carton =160kg
Final Chargeable Weight:
| Total Actual Weight (kg) | Total Volume Weight (kg) | Chargeable Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 120 | 160 | 160 (Volume Weight) |
Since the volume weight (160 kg) is greater than the actual weight (120 kg), the chargeable weight is 160 kg.
Key Differences Between Chargeable & Gross Weight
| Factor | Gross Weight | Chargeable Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actual weight including packaging | Billing weight used for shipping cost |
| How It’s Measured? | Weighing scale | Comparison between Gross and Volume Weight |
| Formula Used | Total physical weight | (L × W × H) ÷ 6000 (or 5000 for express) |
| Which One is Used? | For warehouse & handling | For freight cost calculation |
| Which One is Higher? | Often lower | Can be higher if shipment is bulky |
Why is Chargeable Weight Important?
- Shipping Cost Calculation → Determines freight cost.
- Reduces Shipping Surprises → Avoids unexpected high fees.
- Optimized Packing Strategies → Helps minimize shipping costs by reducing volume.
Factors Affecting Chargeable Weight

When calculating shipping costs, understanding the factors that influence chargeable weight is essential. The chargeable weight is determined by comparing the actual weight, also called gross weight, and the volume weight, also called dimensional weight. The higher value is used for billing.
Below are the key factors that affect chargeable weight in international shipping.
1. Type of Freight Service Used
Different shipping methods use different volume weight formulas, which can impact the chargeable weight.
| Shipping Method | Volume Weight Formula |
|---|---|
| Air Freight | (Length × Width × Height) ÷ 6000 |
| Sea Freight | (Length × Width × Height) ÷ 1000 (CBM) |
| Express Shipping (DHL, FedEx, UPS) | (Length × Width × Height) ÷ 5000 |
| Railway Freight | (Length × Width × Height) ÷ 6000 |
Example Calculation
A package with dimensions 100 × 80 × 60 cm
- Air Freight Volume Weight = (100 × 80 × 60) ÷ 6000 = 80 kg
- Express Volume Weight = (100 × 80 × 60) ÷ 5000 = 96 kg
- Sea Freight CBM = (100 × 80 × 60) ÷ 1000000 = 0.48 CBM
The shipping method selected determines the chargeable weight.
2. Dimensions of the Package

- Bulky items with low actual weight result in higher volume weight, increasing chargeable weight.
- Compact, dense items usually have a higher gross weight, which is used as chargeable weight.
Example
| Package Type | Dimensions (cm) | Gross Weight (kg) | Volume Weight (kg) | Chargeable Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small but heavy | 40 × 40 × 40 | 30 | (40×40×40) ÷ 6000 = 10.67 | 30 (Gross Weight) |
| Large but light | 100 × 80 × 60 | 25 | (100×80×60) ÷ 6000 = 80 | 80 (Volume Weight) |
3. Packaging Material and Method
- Excessive packaging increases dimensions and volume weight.
- Compact and optimized packaging reduces space and minimizes chargeable weight.
- Use of pallets adds extra weight and volume.
To lower shipping costs, optimize packaging to reduce unnecessary volume.
4. Consolidation vs. Individual Shipments
- Consolidating multiple small packages can reduce the chargeable weight by optimizing space.
- Shipping items individually may lead to a higher overall chargeable weight due to inefficient space usage.
Using consolidation services to combine multiple shipments into one efficiently packed load can help reduce costs.
5. Shipping Route and Destination
- Different airlines, courier services, and sea freight carriers may apply different volume weight divisors.
- Some regions charge higher shipping rates based on weight breakpoints.
Example
| Destination | Chargeable Weight Rule |
|---|---|
| USA | Uses 6000 divisor for air freight |
| Europe | Uses 5000 divisor for express |
| Australia | Stricter CBM-based sea freight pricing |
6. Special Handling Requirements
- Fragile items may require additional padding, increasing the package size.
- Irregularly shaped cargo may take up more space than expected.
- Heavy-duty crates for machinery or industrial goods add weight and volume.
Strategies to Reduce Shipping Costs

- Optimize Packaging – Use compact, space-efficient packaging to reduce volume weight.
- Use Vacuum Packing – For soft items like clothing or pillows, vacuum packing can lower volume weight significantly.
- Choose the Right Shipping Method – For bulky but lightweight shipments, sea freight may be more cost-effective.
- Negotiate with Freight Forwarders – Some forwarders offer discounts for high-volume shipments.
- Consider Consolidation Services – Combine multiple shipments to reduce overall volume weight.
You May Interested in Top 11 Tips to Save Alibaba Shipping Costs
Case Study: How DFH Logistics Helped a Client Reduce Shipping Costs
This client buy from Different suppliers, We helped consolidation and repackaging then send together. Make there without any waste space.

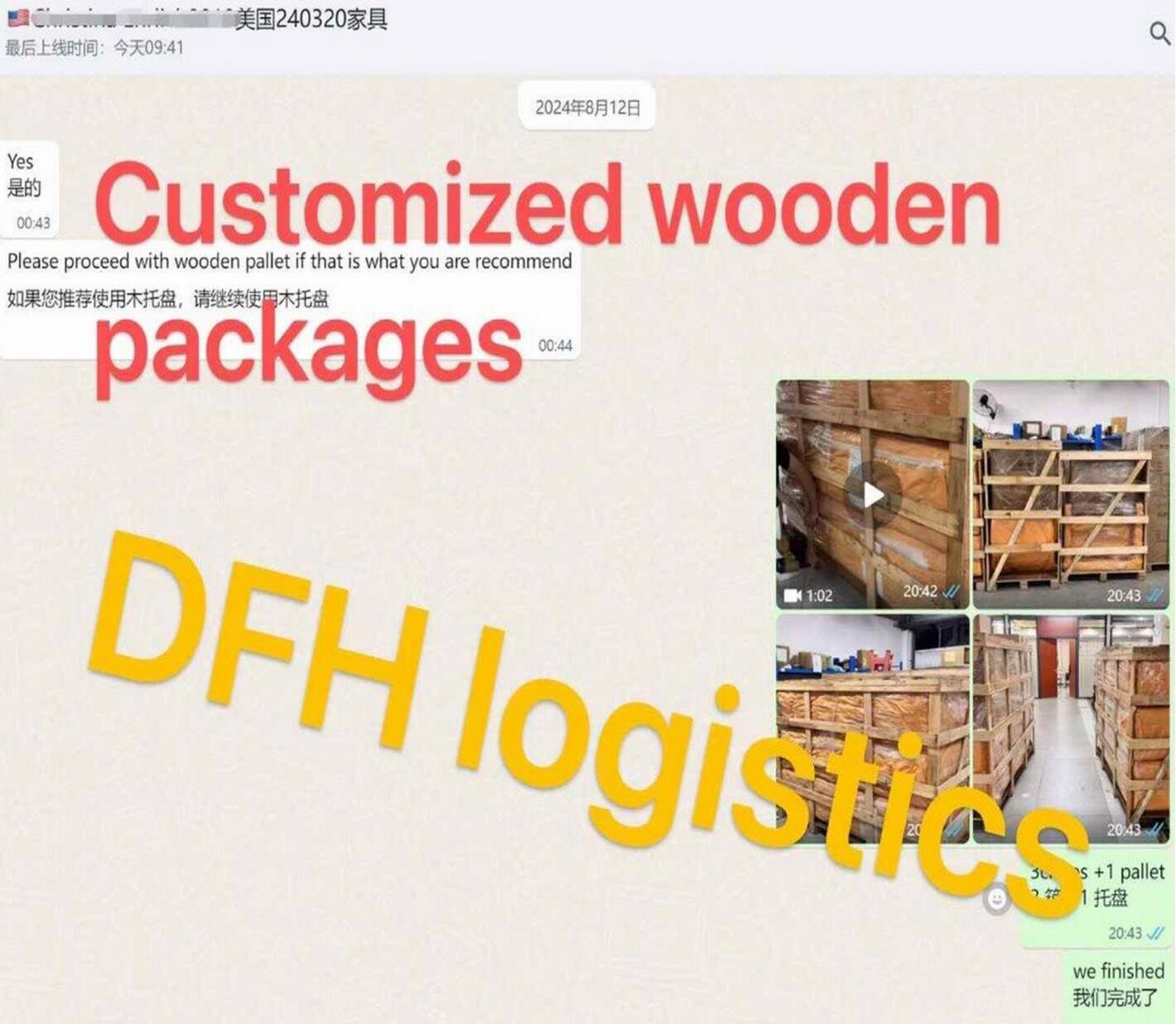
And Finaly, we helped save 608USD for this shipment for this client by mix packing the items and save space. He is very happy with our free charge extra services. and introduced many clients to our company.
Conclusion
Understanding chargeable weight vs. volume weight is essential for importers looking to manage logistics expenses effectively. Choosing the right shipping method and optimizing packaging can significantly reduce costs.
Need Help with Shipping from China?
DFH Logistics specializes in air freight, sea freight, express courier, and DDP shipping solutions. Contact us today for a free shipping quote!




